Answer:
Option A
Explanation:
Given, a toroid with a rectangular cross-section of inner radius a and outer radius b.
Height of the solenoid=h
Magnetic field inside a rectangular toroid is given by
$B=\frac{\mu_{0}n^{}I}{2 \pi r}$ ................(i)
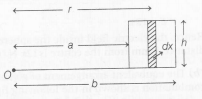
Using the infinitesimal cross-sectional area element,
dx=h dr
$\therefore$ Flux passing through the cross-section of toroid
$\phi=\int B.dx =\int_{a}^{b} \frac{\mu_{0}n^{}I}{2 \pi r}.(h dr)$
$\phi= \frac{\mu_{0}n^{}Ih}{2 \pi }\int_{a}^{b} \frac{1}{r}. dr$
$\Rightarrow$ $\phi= \frac{\mu_{0}n^{}Ih}{2 \pi }[\log r]_{a}^{b}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\phi= \frac{\mu_{0}n^{}Ih}{2 \pi } (\log b-\log a)$
$\phi= \frac{\mu_{0}n^{}Ih}{2 \pi }ln\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)$
Now, self inductance of rectangular toroid.
$L= \frac{n \phi}{I}$
Putting the value of $\phi_{}$ , we get
L= $\frac{\mu_{0}n^{2}h}{2 \pi}ln\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)$