Answer:
Option D
Explanation:
Focal length of the diverging lens is 25 cm.
As the rays are coming parallel, so the image (I1) will be formed at the focus of diverging lens i.e., at 25 cm towards left of diverging lens
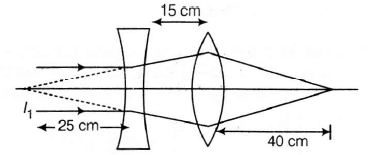
Now, the image (I1) will work as an object for a converging lens.
For a converging lens, the distance of object u (i.e, the distance of I1) = -(25+15)
= -40 cm
f = 20 cm
$\therefore$ From lens 's formula
$\frac{1}{f}= \frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}$
$\frac{1}{20}= \frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{-40}\Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{40}$
$\frac{1}{v}= \frac{1}{90}\Rightarrow v =40 cm$
v is positive so image will be real and will form at right side of converging lens at 40 cm.