Answer:
Option B
Explanation:
Let $f(x)=\int_{0}^{x} \frac{t^{2}}{1+t^{4}}dt$
$\Rightarrow f'(x)=\frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{4}}>0$ , for all $x \epsilon [0,1]$
$\therefore$ f(x) is increasing
At x=0, f(0)=0 and x=1,
$f(1)=\int_{0}^{1} \frac{t^{2}}{1+t^{4}}dt$
Because, $0<\frac{t^{2}}{1+t^{4}}<\frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\int_{0}^{1} 0.dt <\int_{0}^{1} \frac{t^{2}}{1+t^{4}}dt<\int_{0}^{1} \frac{1}{2}.dt$
$\Rightarrow$ $0<f(1)<\frac{1}{2}$
Thus, f(x) can be plotted as,
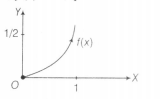
$\therefore$ y= f(x) and y=2x-1 can be shown as
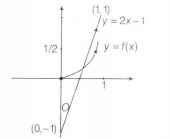
From the graph , the total number of distinct solutions for $x \epsilon [0,1]$ = 1
[ as they intersect only at one point]