Answer:
Option A,D
Explanation:
Given, $(x^{2}+xy+4x+2y+4)\frac{\text{d}y}{\text{d}x}-y^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $[(x^{2}+4x+4)+y(x+2)]\frac{dy}{dx}-y^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $[(x+2)^{2}+y(x+2)]\frac{dy}{dx}-y^{2}=0$
Put x+2=X and y=Y, then
$(X^{2}+XY)\frac{dY}{dX}-Y^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $X^{2}dY+XYdY-Y^{2}dX=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $X^{2}dY+Y(XdY-YdX)=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $-\frac{dY}{Y}=\frac{XdY-YdX}{X^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ $-d(\log|Y|)=d(\frac{Y}{X})$
On integrating both sides , we get,
$-\log|Y|=\frac{Y}{X}+C$
where x+2=X and y=Y
$\Rightarrow$ $-\log|y|=\frac{Y}{x+2}+C$ ...........(i)
Since, it passes through the point (1,3)
$\therefore$ $-\log 3 =1+C$
$\Rightarrow$ $C =-1-\log 3$
$=-(\log e +\log 3)$
$=-\log 3e $
$\therefore$ Eq. (i) becomes
$\log |y|+\frac{y}{x+2} -\log (3e)=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $\log\left( \frac{|y|}{3e}\right)+\frac{y}{x+2}=0$ ........(ii)
Now, to check option (a) y=x+2 intersects the curve.
$\Rightarrow$ $\log (\frac{|x+2|}{3e})+\frac{x+2}{x+2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $\log (\frac{|x+2|}{3e})=-1$
$\frac{|x+2|}{3e}=e^{-1}=\frac{1}{e}$
$\Rightarrow$ ${|x+2|}=3 $ or $x+2=\pm3$
$\therefore$ x=1, -5 (rejected) , as x>0 [given]
$\therefore$ x=1 only one solution
Thus ,(a) is the correct answer.
To check option (c) we have
$y=(x+2)^{2}$
and $\log(\frac{|y|}{3e})+\frac{y}{x+2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $\log\left[\frac{|x+2|^{2}}{3e}\right]+\frac{\left(x+2\right)^{2}}{x+2}=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $\log\left[\frac{|x+2|^{2}}{3e}\right]=-\left(x+2\right)$
$\Rightarrow$ $\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{3e}=e^{-(x+2)}$
or $(x+2)^{2}.e^{x+2}=3e$
$\Rightarrow$ $e^{x+2}=\frac{3e}{(x+2)^{2}}$
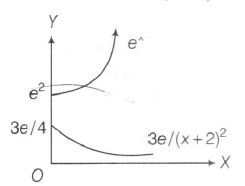
Clearly, they have no solution.
To check option (d),
$y=(x+3)^{2}$
i.e, $\log \left[ \frac{|x+3|^{2}}{3e}\right]+\frac{(x+3)^{2}}{(x+2)}=0$
To check the number of solutions,
Let $g(x)= 2\log (x+3)+\frac{(x+3)^{2}}{(x+2)}-\log (3e)$
$\therefore$ $g'(x)=\frac{2}{x+3}+$
$\left( \frac{(x+2).2(x+3)-(x+3)^{2}.1}{(x+2)^{2}}\right)-0$
$=\frac{2}{x+3}+\frac{(x+3)(x+1)}{(x+2)^{2}}$
Clearly, when x>0, then ,g' (x)>0
$\therefore$ g(x) is increasing , when x>0
Thus ,when x.0, then g(x) >g(0)
$g(x)>\log (\frac{3}{e})+\frac{9}{4}>0$
Hence, there is no solution
Thus, option (d) is true