Answer:
Option B,C
Explanation:
Let θ be the angle between ˆu and →v
∴|ˆu×→v|=1⇒|ˆu|→v|sinθ=1
∴|→v|sinθ=1 [∴|ˆu|=1] .......(i)
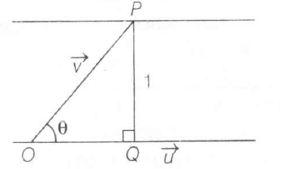
Clearly, there may be infinite vectors
→OP=→v , such that P is always 1 unit distance from ˆu.
∴ Option (b) is correct.
Again, let Φ be the angle between ˆw and ˆu×→v.
∴ˆw.(ˆu×→v)=1⇒|ˆw||ˆu×→v|cosϕ=1
⇒cosϕ=1⇒ϕ=0
Thus, ˆw=ˆu×→v
Now, if ˆu lies in XY-plane, then
|ˆiˆjˆku1u20v1v2v3|
or ˆu=uˆi+u2ˆj
∴ˆw=(u2v3)ˆi−(u1v3)ˆj+(u1v2−v1u2)ˆk
∴ˆw=1√6(ˆi+ˆj+2ˆk)
∴ u2v3=1√6⇒u1v3=−1√6
⇒u2v3u1v3=−1 or |u1|=|u2|
∴ Option (c) is correct.
Now, if ˆu lies un XZ-plane, then ˆu=u1ˆi+u3ˆk
∴
|ˆiˆjˆku10u3v1v2v3|
⇒w=(−v2u3)ˆi−(u1v3−u3v1)ˆj+(u1v2)ˆk
⇒ˆw=1√6(ˆi+ˆj+2ˆk)
=−v2u3=1√6 and u1v2=2√6
=|u2|=2|u3|
∴ Option (d) is incorrect