Answer:
Option C
Explanation:
Here, {(x,y)}ε R2:y≥√∣x+3∣,5y≤(x+9)≤15 }
∴y≥√x+3
⇒ y≥{√x+3,whenx≥−3√−x−3whenx≤−3
or y2≥{x+3whenx≥−3−3−xwhenx≤−3
shown as
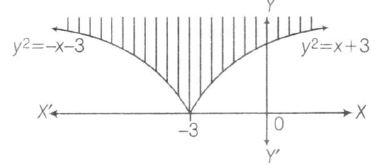
Also, 5y≤(x+9)≤15
⇒ (x+9)≥5y and x≤6
shown as
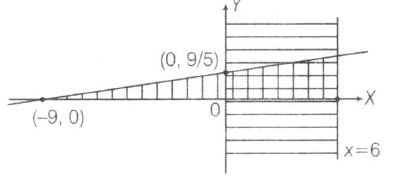
∴ { (x,y)ϵR2:y≥√∣x+3∣,5y≤(x+9)≤15}
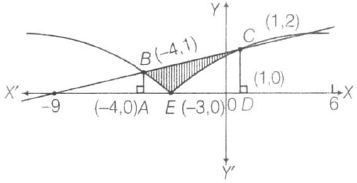
∴ Required area
= Area of trapezium ABCD - Area of ABE under parabola- Area of CDE under parabola
= 12(1+2)(5)−∫−3−4√−(x+3)dx−∫1−3√(x+3)dx
=152−[(−3−x)32−32]−3−4−[(x+3)3232]1−3
=152+23[0−1]−23[8−0]
=152−23−163=152−183=32