A frame of the reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial frame of reference is called a non- inertial frame of reference. A coordinate system fixed on a circular disc rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular velocity ω is an example of a non-inertial frame of reference. The relationship between the force →Frot experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force →Fin experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is,
→Frot=→Fin+2m(→vrot×→ω)+m(→ω×→r)×→ω
where, Vrot is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and r is the position vector of the particle with respect to center of the disc
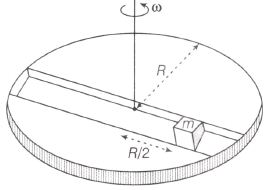
Now, consider a smooth slot along a diameter of a disc of radius R rotating counter-clockwise with a constant angular speed ω about its vertical axis through its centre. We assign a coordinate system with the origin at the centre of the disc, the X-axis along the slot, the Y-axis perpendicular to the slot and Z-axis along the rotation axis((ω=ωˆk). A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at r=(R2)ˆi at t=0 and is constrained to move only along the slot
The net reaction of the disc on the block is