Answer:
Option B
Explanation:
Central Idea Consider cavity as negative mass and apply superposition of gravitatiional potential.
Consider , the cavity formed in a solid sphere as shown in figure
V(∞)=0
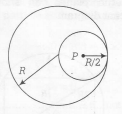
According to the question, we can write potential at an internal point P due to the complete solid sphere.
Vs=−GM2R3[3R2−(R2)2]
=−GM2R3[3R2−R24]
=−GM2R3[11R24]=−11GM8R
Mass of removed part
=M43×πR3×43×π(R2)3=M8
Potential at point P due to removed part
Vc=−32×GM/8R2=−3GM8R
Thus, potential due to remaining part at point P.
Vp=Vs−Vc=−11GM8R−(−3GM8R)
=(−11+3)GM8R=−GMR