Answer:
Option B
Explanation:
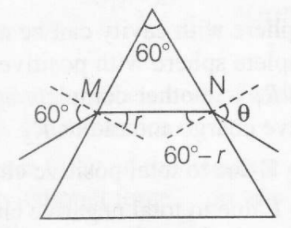
Appluing Snell's law at M and N,
$ \sin60^{0}=n\sin r$ ............(i)
$\sin\theta=\pi\sin(60-r)$ ............(ii)
Differentiating we get
$\cos\theta\frac{d\theta}{dn}=-n\cos(60-r)\frac{dr}{dn}+\sin(60-r)$
Differentiating Eq.(i),
$n\cos r\frac{dr}{dn}+\sin r=0$
or $\frac{dr}{dn}=-\frac{\sin r}{n\cos r}=\frac{-\tan r}{n}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\cos \theta \frac{d\theta}{dn}=-n\cos(60^{0}-r)\left[\frac{-\tan r}{n}\right]+\sin(60^{0}-r)$
$\frac{d\theta}{dn}=\frac{1}{\cos\theta}\left[ \cos(60^{0}-r\right)\tan r+\sin(60^{0}-r)]$
From Eq.(i) , r =30° for n=$\sqrt{3}$
$\frac{d\theta}{dn}=\frac{1}{\cos 60}(\cos 30\times \tan 30+\sin 30)$
$=2(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2})=2$