Answer:
Option A
Explanation:
Put t= x -[x]={X}, which is a fractional part function and lie between 0≤{x} <1 and then solve it,
Given a ε R and equation is
-3(x-[x])2+2(x-[x])+a2=0
t=x-[x] , then equation is
−3t2+2t+a2=0
⇒ t=1±√1+3a23
∴ t= x-[x]= {X}
{ fractional part}
∴ 0≤t≤1
0≤1±√1+3a23≤1
Taking positive sign , we get
0≤1+√1+3a23<1 [ ∴ {x}>0}
⇒ √1+3a2<2⇒1+3a2<4
⇒ a2-1<0
⇒ (a+1)(a-1)<0
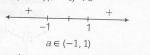
for no integral solution of a we consider the interval (-1,0) ∪ (0,1) .
Note. here, we figure out the integral solution , we get a=0, This implies any interval excluding zero should be correct answer as it gives either no solution or no integral.