Answer:
Option A
Explanation:
(P) y=cos(3cos−1x)
y′=3sin(3cos−1x)√1−x2
√1−x2y′=3sin(3cos−1x)
⇒ −x√1−x2y′+√1−x2 y''
= 3cos(3cos−1x).−3√1−x2
⇒ −xy′+(1−x2)y″=−9y
⇒ 1y[(x2−1)y′+xy′]=9
(Q) Plan
(i) Angle subtended by a side of n sided regular polygon at the centre = 2πn
(ii) |a xb|=|a||b| sinθ
(iii) |a.b|=|a||b| cosθ
(iv) tanθ=tanα⇒θ=nπ+α,nϵZ
consider a polygon of (S) n sides with centre at origin
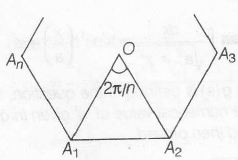
Let |OA1|=|OA2|=......|OAn|
=r(say)
|ak x ak+1|= r2sin2πn
|ak .ak+1|= r2cos2πn
⇒|∑n−1k=1ak×ak+1|=|∑n−1k=1ak.ak+1|
⇒ r2(n−1)sin2πn=r2(n−1)cos2πn
tan2πn=1
⇒ tan2πn=tanπ4
⇒ 2πn=tπ+π4,tϵZ
⇒ 2n=4t+14
⇒ n=84t+1,tϵZ
⇒ the minimum value of n=8
(R) Plan Equation of normal at the point
(acosθ,bsinθ) of ellipse x2a2+y2b2=1 is
given by
axsecθ−bycosecθ=a2−b2
Equation of normal is
√6xsecθ−√3ycosecθ=3
Its slope is
√6secθ√3cosecθ=1
( ∴ slope of normal = slope of line perpendicular to
x+y=8
tanθ=1√2
So, normal is
√6×√3√2−√3×√3y=3
3x-3y=3
⇒ x-y=1
As it passes through (h,l)
So, h-1=1
h=2
(S) Plan
tan−1x+tan−1y=tan−1(x+y1−xy)
Given equation,
tan−1(12x+1)+tan−1(14x+1)=tan−1(2x2)
= tan−1(12x+1+14x+11−1(2x+1)(4x+1))=tan−1(2x2)
⇒tan−1(6x+2(2x+1)(4x+1)−1)=tan−1(2x2)
⇒ 3x+14x3+3x=2x2
⇒ 3x3+x2=8x2+6x
⇒ x(3x2−7x−6)=0
⇒ x(x−3)(3x+2)=0
⇒ x=0,−23,3
So, only positive solution is x=3
P:(iv), Q:(iii), R:(ii), S(i)