Answer:
Option A,B,D
Explanation:
Plan This problem can be solved by using the concept of H-bonding and applications of H-bonding
(a) Ice floats in water due to the low density of ice as compared to water which is due to open cage-like structure (formed by intermolecular H-bonding)
(b) Basic strength of RNH2 >R3 N. It is also explained by hydrogen bonding

Two H- bonds are possible with water present in aqueous solution. (stabilize by solvation)
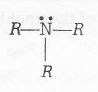
No H bonding is possible with water present in aqueous solution.(stabilization by solvation is very less)
(c)
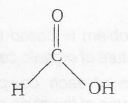
More acidic due to the presence of H. (Due to the absence of electron-donating group)
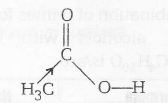
Less acidic than HCOOH due to presence of CH3-
(Electron donating group)
(d) Dimerisation of acetic acid in benzene is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding
