Answer:
Option C,D
Explanation:
$ \mu_{2}$ can never be zero for maximum equilibrium.
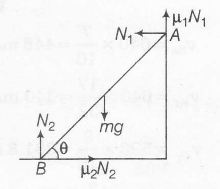
when $\mu_{1}$ = 0 we have
$N_{1}=\mu_{2}N_{2}$ ..........(i)
$N_{1}=m_{2}g$ ...........(ii)
$\tau_{B}=0\Rightarrow mg\frac{L}{2}\cos\theta=N_{1}L\sin\theta$
$\Rightarrow $ $N_{1}=\frac{mg \cot \theta}{2}$
$\Rightarrow$ $ N_{1}\tan \theta=\frac{mg }{2}$
when $\mu_{1}\neq 0$ we have
$\mu_{1}N_{1}+N_{2}=mg$ ........(i)
$\mu_{2}N_{2}$= N .......(ii)
$\Rightarrow$ $ N_{2}=\frac{mg}{1+\mu_{1}\mu_{2}}$