Answer:
Option D
Explanation:
plan when different number of electrons are involved in a redox reaction
$\triangle G^{0}_{net}=\triangle G^{0}_{1}+\triangle G^{0}_{2}$
$-n_{3}FE^{0}_{3}=-n_{1}FE^{0}_{1}-n_{2}FE^{0}_{2}$
$E^{0}_{3}=\frac{n_{1}E^{0}_{1}+n_{2}E^{0}_{2}}{n_{3}}$
(P) $E^{0}_{3+}Fe^{3+}/Fe$
Net reaction
Fe3+→ Fe
is obtained from $\underline{n E^{0}}$
Fe3++e-→ Fe 2+ n1= 1, $ E^{0d}_{1}=0.77V$
$Fe^{2+}+2e^{-}\rightarrow Fe , n_{2}=2, E^{0}_{2}=-0.44V$
$\because$ $Fe^{3+}+3e^{-}\rightarrow Fe , n_{3}=3, E^{0}_{3}=?$
$E^{0}_{3}= \frac{n_{1}E^{0}_{1}+n_{2}E^{0}_{2}}{n_{3}}$
= $E^{0}_{3}= \frac{0.77+2(0.44)}{3}=\frac{-0.11}{3}=-0.04 V$
Thus , P- (3)
Net reaction
$4H_{2}O\rightleftharpoons 4H^{+}+4OH^{-}$
is obtained from $\underline{n E^{0}}$
$2H_{2}O\rightarrow O_{2}$ n1=4 Eo= -1.23 V
+ 4H++4e-
$2H_{2}O+O_{2}+4e^{-}\rightarrow 4OH^{-}$ n2=4 Eo=+0.40V
$4H_{2}O\rightarrow 4H^{+}+4e^{-}$ n3= 4 Eo= ?
$E_3^0=\frac{n_{1}E_1^0+n_{2}E_2^0}{n_{3}}=E_1^0+E_2^0$
=-1.23+0.40= -0.83 V
thus Q-(4)
(R)
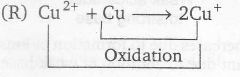
Reduction
for thus E° of Cu2+ → Cu+
is also required. $\underline{n E^{0}}$
Cu2++2e- → Cu n= 2 Eo= 0.34 V
Cu → Cu+ +e- n=1 Eo= -0.52 V
Cu2+ + e- → Cu+ $E_3^0$ ?
$E_3^0=\frac{n_{1}E_1^0+n_{2}E_2^0}{n_{3}}$
$=\frac{2\times 0.34+1\times (0.52)}{1}=0.16 V$
Thus $\underline{n E^{0}}$
Cu→ Cu++e- n1 =1 Eo= -0.52 V
Cu2+ + e-→ Cu+ n2 =1 Eo= 0.10 V
Cu2+ +Cu→ 2Cu+
E0= -0.52 +0.16= -0.36 V
thus (R) - (1)
(S) Cr3+→ Cr2+
is obtained from $\underline{n E^{0}}$
Cr3++3e-→ Cr n= 3 Eo= -0.74 V
Cr→ Cr2+ +2e- n=2 Eo=+0.91 V
Cr3++e-→ Cr2+ n=1 Eo= ?
$E_3^0=\frac{-0.74 \times3+2\times0.91}{1}=0.4 V$
Thuus S= (2)
P:3,Q:4,R:1,S:2