Answer:
Option A
Explanation:
Plan spreading out charge by the overlap of an empty p-orbital with an adjacent σ bond is called hyperconjugation. This overlap(the hyperconjugation) delocalised the positive charge on the carbocation, spreading it over a larger volume, and this stabilises the carbocation.
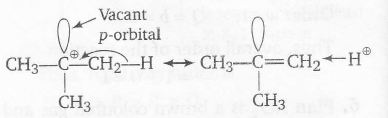
tertiary butyl carbocation has one vacant p-orbital hence, it is stabilised by σ -p (empty) hyperconjugation.
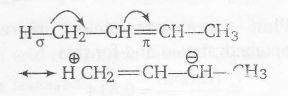
In 2-butene stabilisation is due to hyperconjugation between σ -π∗ electron delocalisations