Answer:
Option A,B,D
Explanation:
Concept involved
(i) Area of region f(x) bounded between x=a to x=b is
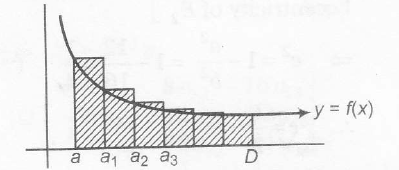
∫baf(x)dx= sum of areas of rectangle shown in shaded part
(ii) if f(x)≥g(x) when defined in [a, b]
⇒ ∫baf(x)dx≥∫bag(x)dx
Description of Situation As the given curve y =e−x2 cannot be integrated thus we
have to bound this function by using above mentioned concept
sol. Graph for , y=e−x2
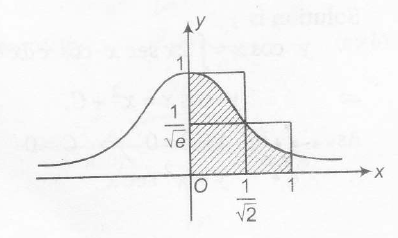
since , x2≤x when xϵ[0,1]
⇒ −x2≥−x or e−x2≥e−x
∴ ∫10e−x2dx≥∫10e−xdx
⇒ S≥−(e−x)10=1−1e........(i)
Also, ∫10e−x2dx≤ area of two rectangle
≤(1×1√2)+(1−1√2)×1√e
≤1√2+1√e(1−1√2)..........(ii)
∴ 1√2+1√e(1−1√2)≥S≥1−1e
[from Eqs.(i) and (ii) ]